Do you find adding the high dose riboflavin has helped you?
Yes, I have proven mutations in my PNPO enzyme. Both
Pyridoxine 5' Phosphate (PNP) and
Pyridoxamine 5' Phosphate (PMP)(Both vitamin B6 vitamers) are
substrates of the
PNPO enzyme, and a derivative of
Riboflavin (vitamin B2), namely,
Flavin Mononucleotide (FMN) acts as the
coenzyme to the
PNPO enzyme. So, for me, they both work together to increase the production of the
product molecule, namely
Pyridoxal 5' Phosphate (PLP, also a vitamin B6 vitamer and the active coenzyme form of vitamin B6 (
PMP is a coenzyme to a lesser degree)).
PNPO - Pyridoxine-5'-phosphate oxidase - Homo sapiens (Human) | UniProtKB | UniProt
Normally the human body obtains enough vitamin B6 and vitamin B2 from a well balanced diet. Normally there are no mutations in your PNPO enzyme to cause any problems. 100% RDA of any vitamin supplement is enough to correct a dietary 'deficiency' in a particular vitamin. (Better still is to alter one's diet to include more foods rich in the vitamin you are deficient in). But 100% RDA of a vitamin is not enough to treat most cases of vitamin 'dependency' - due to a mutated enzyme(s).
Overview of Vitamins - Nutritional Disorders - MSD Manual Professional Edition (msdmanuals.com)
Regarding B6, do you find any help in using both P5P and pyridoxine?
I have never used
PLP with my long 'prescribed'
Pyridoxine Hydrochloride (PN HCl) tablets. Although I have researched it.
PLP can inhibit (interfere with) the action of my PNPO enzyme (due to my PNPO enzyme been mutated the way it is) and may cause my severe seizures (status Epilepticus) to return if I switch from
PN to
PLP. This has occurred in some (few) of the different cases affected with 'PNPO Deficiency'.
PLP, in a very high dose used over long periods of time, may also be responsible for the onset of Cirrhosis of the liver in a few cases of PNPO Deficiency. Also, why change something which is working and is not causing me any problems thus far.
Pyridoxine responsiveness in novel mutations of the PNPO gene - PubMed (nih.gov)
Cirrhosis Associated with Pyridoxal 5′-Phosphate Treatment of Pyridoxamine 5′-Phosphate Oxidase Deficiency - PMC (nih.gov)
Regards the different cases of 'PNPO Deficiency': What works - if at all - and in what combination, all depends on how much the mutation(s) have degraded the PNPO enzyme's ability to function. Also where in the PNPO enzyme the mutation(s) are located can effect its ability to function - very differently. This is true of any mutated enzyme. Different people may have mutations else where, in different enzymes/nonenzymatic proteins to me which affect them in a different way to me. We are all very different and complex when it comes down to our genetics!! My mutations seem to affect the binding of both B6 and B2 to my PNPO enzyme's '
active site' equally.
Pharmacogenomics of Drug Metabolizing Enzymes and Transporters: Relevance to Precision Medicine - PMC (nih.gov)
Phenotypic and molecular spectrum of pyridoxamine‐5′‐phosphate oxidase deficiency: A scoping review of 87 cases of pyridoxamine‐5′‐phosphate oxidase deficiency - PMC (nih.gov)
So in my case: Increased '
PNP' (derived from my
PN HCl tablets) or (PMP) (both B6
substrates) plus increased
FMN (B2
coenzyme) >
*PNPO enzyme* > increased
PLP (product) output to be shared between the more than 100 different enzymes which need
PLP as their coenzyme - including GAD, AADC...etc. The sum of all the enzymes in each of our bodies (very much, if not entirely) equals our metabolism. Enzymes work on a subcellular level.
17.2: Pyridoxal Phosphate (Vitamin B6) - Chemistry LibreTexts
NOTE: The abbreviation '
P5P' can stand for any one of the three vitamin B6,
5'-Phosphate derivatives, namely:
Pyridoxine
5'
Phosphate (
P5P or '
PNP'),
Pyridoxamine
5'
Phosphate (
P5P or '
PMP') or
Pyridoxal
5'
Phosphate (
P5P or '
PLP'). Very confusing. This is why I have chosen to use
PLP over P5P as the abbreviation for [
P]yridoxa[
L] 5' [
P]hosphate
(PLP). Also,
PLP is favoured in the scientific literature. In using this notation, '
Pyridoxine' becomes (
PN),
Pyridoxamine becomes
(PM) and
Pyridoxal, (PL). All (
PN,
PM,
PL,
PNP,
PMP and
PLP) are classed as vitamin B6 'vitamers'.
Vitamin B6 - Health Professional Fact Sheet (nih.gov)
My medication is very tailored to treat my extremely rare and possibly genetically unique condition.
**DO NOT ALTER ANY MEDICATION WITHOUT YOUR DOCTOR'S CONSENT**
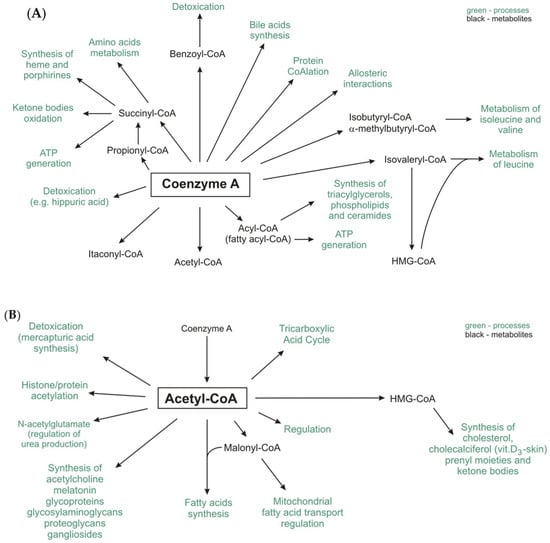
The active form of Pantothenic Acid (vitamin B5, Pantothenate) is 'Coenzyme A' (CoA). Acetyl-CoA works, within our bodies, with Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) to form the two main ketone bodies, acetoacetate (AcAc) and 3-beta-hydroxybutyrate (3HB).
IJMS | Free Full-Text | The Pathophysiological Role of CoA (mdpi.com)
Vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin) does nothing for my seizures also but since it is not doing more good than harm, I continue to use it and all the other vitamins I take as part of my multi vitamin complex on a daily bases.